- Visibility 40 Views
- Downloads 8 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.jooo.2020.034
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Complex odontome in posterior maxilla: A rare occurenc
- Author Details:
-
Latika Bachani *
-
Monika Singh
-
Anshul
-
Ashok Lingappa
Introduction
A 40 years old female patient complained of swelling of face over the cheek region on the right side since 2 months and pain in right upper back jaw region since 1 month. The swelling was insidious in onset, slowly progressing in size, was not associated with any other signs and symptoms. No history of epistaxis, nasal obstruction, headache or visual disturbance was reported. No history of trauma was revealed. Pain was insidious in onset, intermittent, moderate, dull aching type, aggravates on mastication and at night, temporarily relieved on taking over-the-counter medications, radiating to right ear. No history of previous episode of similar pain. Patient reported associated sensitivity in teeth in that region on drinking water. No history of any discharge intra-orally from that region. Her medical history and past dental history were non-significant. She has mixed diet, brushes her teeth once daily with toothbrush and toothpaste and has no abusive habits history.
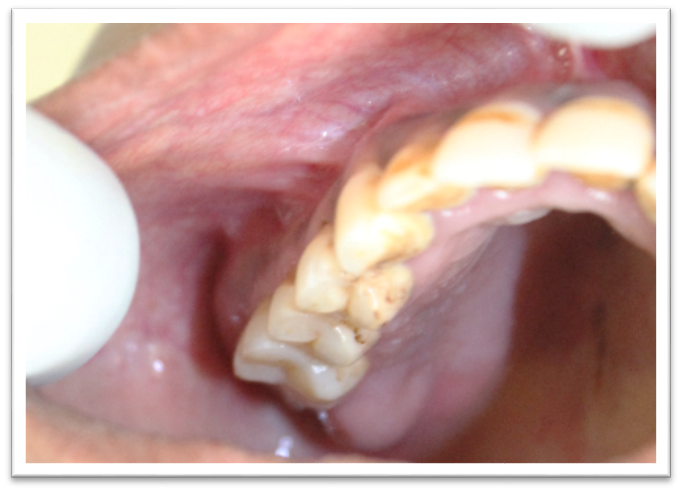
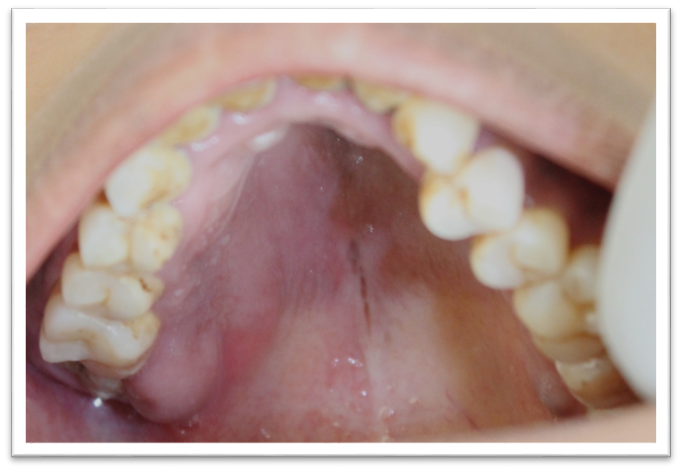
On general physical examination, she was moderately built, well oriented to time, place and person with no signs of pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing and organomegaly. On extra-oral examination, a solitary swelling was noted over the right side of her face involving the middle third ([Figure 2]). It was roughly oval in shape, measuring approx. 5cm in diameter, extending superio-inferiorly from 2cm below infra-orbital margin till the level of corner of the mouth and mesio-distally from ala of the nose till the level of outer canthus of the eye. The borders were diffuse. Skin over it was normal in color as the surrounding skin. Surface was smooth. On palpation, all the inspectory findings were confirmed. The swelling presented with no local rise in temp, was bony hard in consistency, non-tender and skin over it was pinchable. It was non-mobile. Bilateral submandibular lymph nodes were palpable. They were solitary, roughly oval in shape, approx. 1cm in diameter, firm, mobile and tender. On intra-oral examination, the labial mucosae and buccal mucosae were apparently normal ([Figure 3]). Solitary swelling was seen involving the right side of the palate ([Figure 4]). It was roughly oval in shape, measuring approx. 4-5 cm in greatest diameter, extending antero-posteriorly from the level of 15 till maxillary tuberosity and mesio-distally from the palatal gingiva irt 15, 16, 17 and distal to it till approx 2cm short of the midline. The borders were well-defined. The mucosa over it was pink in color. The surface was smooth. On palpation, all inspectory findings were confirmed. It was bony hard in consistency and non-tender. Vestibular obliteration irt 17 and distal to it was noted. Buccal cortical plate expansion was present irt 17 and distal to it ([Figure 3]). The swelling was bony hard on palpation. No mobilty present irt 15, 16 and 17.
On the basis of history and examination, provisional diagnosis of Benign Odontogenic Tumor Involving Right Posterior Maxilla was given. The differentials were listed as:
Benign odontogenic tumors
Odontoma.
Ameloblastoma.
Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT).
Benign non-odontogenic tumors:
Central ossifying fibroma.
Investigations
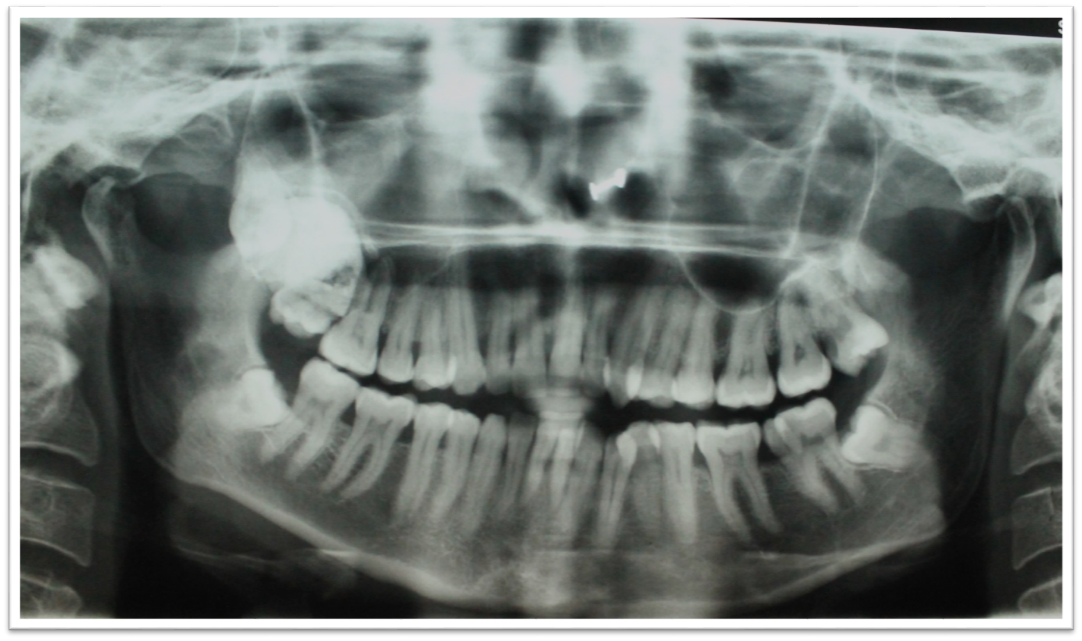
OPG ([Figure 5]) revealed solitary radiopaque lesion roughly oval in shape, measuring approx. 5 cm in diameter, located in the right posterior maxilla. It had well defined borders and was surrounded by a radiolucent rim with a sclerotic border. The internal structure is homogeneously radiopaque. It was covering the root of 17.
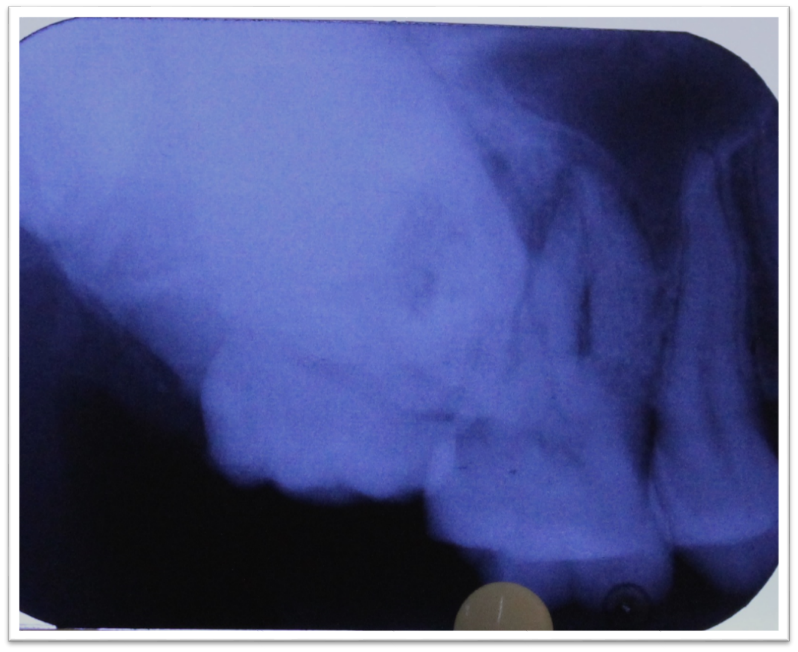
IOPA irt 18 ([Figure 6]) reveals solitary radiopaque lesion roughly oval in shape, measuring approx. 5 cm in diameter, located in the right posterior maxilla. It had well defined borders and was surrounded by a radiolucent rim. The internal structure is homogeneously radiopaque. It was covering the root of 17.
The radiographic differentialswere listed as:
Complex composite Odontoma.
CEOT.
Central ossifying fibroma.
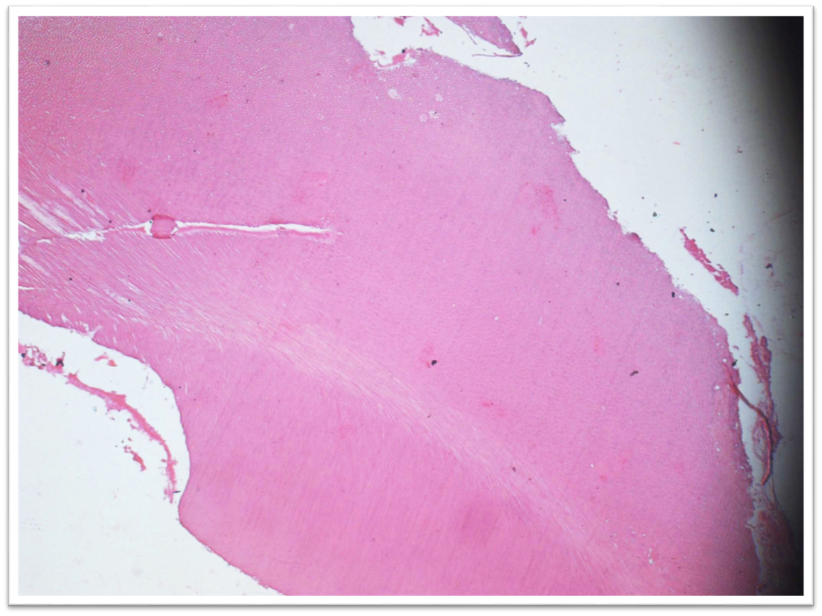
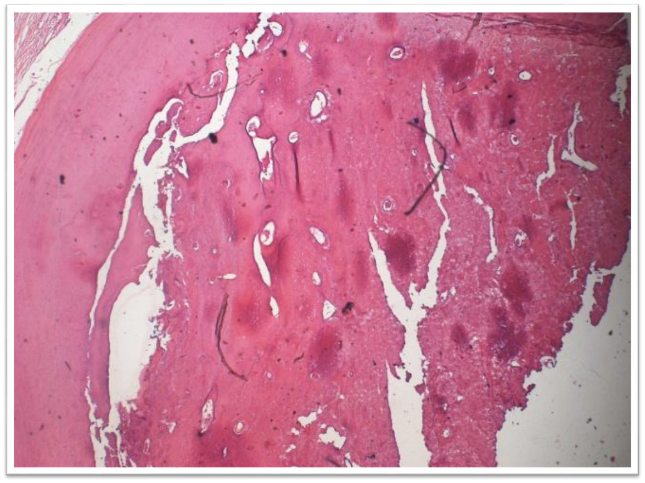
The lesion was managed as excision of the lesion with surgical removal of 18 and and extraction of 17. The biopsy report at 20x, decalcified and H&E stained sections revealed presence of irregular mature tubular dentin enclosing clefts and hollow circular spaces surrounded by a layer of cementum. There was also evidence of connective tissue surrounding the dentin ([Figure 7]).
Hence, the final diagnosis was given as Complex Composite Odontomeirt impacted 18.

Discussion
Odontomes are mixed odontogenic tumorsbecause they have both epithelial and ectomesenchymal components. Both these components are morphologically normal but have defect in their structural arrangement. Hence called as Hamartomas or malformations rather than true neoplasms.[1] The term “odontome” was first coined by Broca in 1866. He defined it as “growth in which both the epithelial and connective tissue components exhibit complete differentiation, with the result that functional ameloblasts and odontoblasts form enamel and dentin”. Still lesion takes place because dental components are laid down in a disorganized manner, due to failure of normal morpho-differentiation.[2] WHO classifies odontomas as a benign odontogenic tumor composed of odontogenic epithelium and odontogenic ecto-mesenchyme with dental hard tissue formation.[3]
Classification
In 1914, Gabell, James, and Payne grouped odontome according to their developmental origin:
Epithelial,
Composite (epithelial and mesodermal), and
Connective tissue.[4]
In 1946, by Thoma and Goldman:
Geminated composite odontomes.
Compound composite odontomes.
Complex composite odontomes.
Dilated odontomes.
Cystic odontomes.[5]
Classification by H.M. Worth:
Ectodermal origin (Enameloma),
Mesodermal origin (dentinoma, cementoma),
Mixed ectodermal and mesodermal origin (complex composite odontome, compound composite odontome, geminated odontome, dilated odontome, including dens in dente).[6]
WHO classification:
Complex odontome.
Compound odontome.
Ameloblastic fibro-odontome.
New type known as hybrid odontome, is also reported by some authors[7]

Compound odontome
Malformations in which all dental tissues are represented in a more orderly pattern, so that the lesion consists of many tooth like structures or denticles composed of enamel, dentin, cementum and pulp.
Several small abnormal teeth surrounded by a fibrous sac.[4]
Compound odontome as classified by Gravey et al.[8]
Complex odontoma
WHO defines it as: “A malformation in which all the dental tissues are represented, individual tissues being mainly well formed but occurring in a more or less disorderly pattern”.[9]
Epidemiology
Odontomas are common odontogenic tumors.
Odontomes: 22%
Complex odontome: 5-30%
Compound odontome: 9-37%[10]
Etiopathogenesis
Unknown etiology.
Various factors attributed to it are:
Odontome can occur in one or more of three ways:
By interference with the mechanism whereby genes control tooth formation and formed.
By a mutation in the genes concerned.
By inheritance of those abnormal genes.
Hitchin proposed
Mutation in the epithelial cells of the tooth germ.
↓
Changes inherent capacity of odontogenic epithelium to go through the cap and bell stages of tooth formation, but retains ability to stimulate mesenchymal differentiation to form functional ameloblasts and odontoblasts.
↓
Formation of an odontoma.[11]
Clinical features
Age: peak in the 2nd decade of life.
Sex: Male: Female ratio: 1.5:1 - 1.6:1.e.
Site: anterior maxilla > posterior mandible.
Size: varies from that of a walnut, or even larger, to a size that is only microscopically detectable.[10].
Asymptomatic.
Clinical indicators of odontoma: retention of deciduous teeth, non-eruption of permanent teeth, pain, expansion of the cortical bone and tooth displacement.
Other symptoms include paresthesia and swelling.[12]
Odontomas located in the anterior maxillary region are compound, while odontomas located in the posterior mandible region are complex odontomas.[13]
Compound odontomas seldom cause bony expansion but complex odontomes often cause slight or even marked bony expansion.[14]
Syndromes associated
Gardner syndromee
Hermann syndromes
Familial colonic adenomatosis
Basal cell nevus syndrome[15]
Radiologically
It has three stages depending on the amount of calcification.
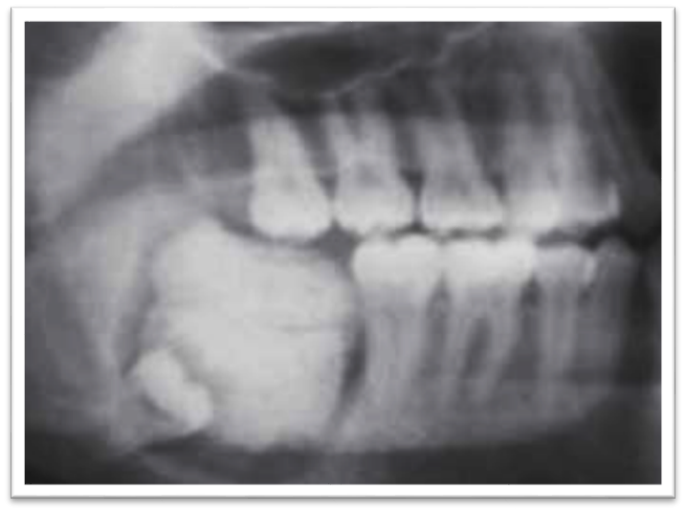
Complex odontome appears as a radiopacity situated in the bone, having density greater than that of bone and equal or greater than that of tooth surrounded by a radiolucent halo ([Figure 9]).
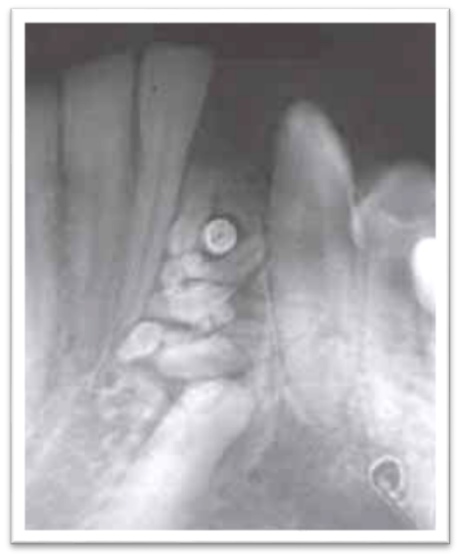
Two appearances of compound odontome are ([Figure 10]):a. Cluster of small shapeless dense masses having no resemblance to a tooth in shape but equal or greater in density, depending upon the size of the mass.b. Presence of two or more tooth like masses having conical enamel like capped crowns and with fusion of radiolucent portions.[16]
Histopathology ([Figure 11])
Well-delineated, roughly spherical mass of a haphazard conglomerate of mature hard dental tissues.
The degree of morphodifferentiation varies from lesion to lesion.
There is predominantly dentine of an irregular variety, cementum or cementum-like tissue in small amounts and there is an admixture of dentine with round or ovoid spaces containing pulp tissue, enamel epithelium and remnants of enamel matrix.[9]
Management
Complex odontomas can be associated with other more aggressive odontogenic lesions such as cysts and tumors.
Hence, once detected, it should be surgically removed.
Conservative surgical enucleation: treatment of choice.[1]
Conclusion
Odontome is a common lesion to occur in the jaws. Radiopacities in the posterior maxilla can include odontome as one of the differentials considering the location, association with a missing tooth and the radiographic appearance of the lesion. Hence, as an oral physician and radio-diagnostician, we should know the clinical features and radiographic appearance of this lesion.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- K M Thoma, H M Goldman. . Oral Pathology 1960. [Google Scholar]
- H Philipse, P A Reichart, F Praetorius. Mixed odontogenic tumours and odontomas. Considerations on interrelationship. Review of the literature and presentation of 134 new cases of odontomas. Oral Oncol 1997. [Google Scholar]
- P J Slootweg. An analysis of the interrelationship of the mixed odontogenic tumors—ameloblastic fibroma, ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, and the odontomas. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol 1981. [Google Scholar]
- F Praetorius, A: Piatelli, L Barnes, J W Eveson, P Reichart. WHO Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumour . Odontoma 2005. [Google Scholar]
- L Junquera, J C De Vicente, P Roig. Intraosseous odontoma erupted into the oral cavity: An unusual pathology. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2005. [Google Scholar]
- H M Worth. . Principles and practice of oral radiologic interpretation 1963. [Google Scholar]
- I R Kramer, J J Pindborg, M Shear. . Histological Typing of Odontogenic Tumour. WHO. International Histological Classification of Tumours 1992. [Google Scholar]
- V Satish, M C Prabhadevi, R Sharma. Odontome: A Brief Overview. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2011. [Google Scholar]
- S Or, S Yucetas. Compound and complex odontomas. Inter J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1987. [Google Scholar]
- P Gurdal, T Seckin. Odontomas. Quintessence Int 2001. [Google Scholar]
- G E Kaugars, M E Miller, L M Abbey. Odontomas. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol 1989. [Google Scholar]
- S A Cuesta, J G Albiol, L B Aytés, C G Escoda, Gay Escoda, C. Review of 61 cases of odontoma. Presentation of an erupted complex odontoma. Med Oral 2003. [Google Scholar]
- R W Katz. An analysis of compound and complex odontomas. ASDC J Dent Child 1989. [Google Scholar]
- E C Stafne, J A Giblisco. . Oral roentgenographic diagnosis 1975. [Google Scholar]
- O Hidalgo-Sánchez, M I Leco-Berrocal, J M Martínez-González. Meta-analysis of the epidemiology and clinical manifestations of odontomas. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2008. [Google Scholar]
- R M Kodali, B V suresh, P R Raju, S K Vora. An Unusual Complex Odontoma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2010. [Google Scholar]
