Introduction
Mandibular third molar is the most common impacted tooth removed routinely in dental office.1 Impacted mandibular third molars are classified by Winter taking angulation of mandibular second molars into consideration.2 Mesioangular impactions are the most common among them.3
Proper skill and adequate experience are required for the surgical removal of impacted third molars in order to avoid undesirable complications. The surgeon has to deal with a limited space as there is tongue and cheek adjacent to the surgical area that require proper retraction for adequate accessibility. Adjacent tooth and retro molar tissues again limit the access. Appropriate handling of the soft tissues and protection of adjacent vital structures such as adjacent tooth, inferior alveolar and lingual nerve are of importance while attempting the surgical removal of impacted third molars. Every surgeon must be aware of the post-operative complications associated with the surgical removal of impacted third molars which include trismus, dry socket, paraesthesia, oedema, Temporomandibular joint problems and trauma to adjacent tooth.4 It is imperative that the operating surgeon is capable of managing the post-operative complications as well.
Bone removal is one of the important steps in surgical removal of impacted teeth. The amount of bone removed varies according to the type of impaction. Excess removal of bone can lead to unfavorable outcomes such as fracture of the mandible. “Tooth belongs to surgeon and bone belongs to patient.” This statement is enough to explain the importance of odontectomy in the surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars. It helps in removing the tooth in fragments, thus preserving the sound bone and anatomical structures of importance.5 The tooth sectioning varies according to the type of impaction and preference of the surgeon. Longitudinal and cross-sectional methods of sectioning the tooth are the much discussed techniques regarding the removal of mesioangular impacted mandibular third molars.6 Both of these techniques have significant role in total time of surgery and post-operative complications like post-operative edema, trismus, pain and impairment of neuro vasculature.
In this study, longitudinal and cross-sectional methods of tooth sectioning were compared, to help the clinicians choose the appropriate technique, thus reducing operating time and post-operative complications.
Materials and Methods
A total of 50 patients with mesioangular impacted mandibular third molars were included in our prospective study. Only those patients with impacted mandibular third molars on their right side were selected and performed by a single surgeon to avoid operator bias. Patients having mandibular third molars with fused roots, incompletely formed roots, under pre-operative analgesic and antibiotic coverage, were excluded from the study. They were divided into group A (cross-sectional odontectomy) and group B (longitudinal odontectomy) by random allocation. Institutional ethics approval was attained, and informed written consent obtained from all patients.
Thorough history was taken and routine extra oral and intra oral examination was done for all patients. In our study, patients with pericoronitis or caries of mesioangular impacted third mandibular molars were excluded and only those who required disimpaction as a part of their orthodontic treatment or orthognathic surgical work up were included. Orthopantomogram was taken for all the patients and the impacted third molars were classified according to Pell and Gregory classification. Class III and position C type of impacted mandibular third molars were excluded from this study as it needs extensive removal of bone and can affect the final result of the study. The distance from tragus to angle of mouth (Dimension A) and the distance from lateral canthus to angle of mandible (Dimension B) were measured using a measuring tape for the purpose of evaluation of edema post-operatively with the baseline recordings for each technique. Interincisal distance at maximal mouth opening was measured.
All the patients underwent surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars by a single operator under adequate local anaesthesia. Ward’s incision was used in all cases followed by elevation of mucoperiosteal flap. High speed, high torque straight micromotor handpiece and bur (No 703 straight fissure bur) technique was used for bone removal along with copious saline irrigation. Once the crown had been located, the buccal surface of the tooth was exposed to the cervical level of the crown contour and a buccal trough was created.
Tooth sectioning and delivery
Tooth sectioning was done with the same straight no.703 fissure bur along with copious saline irrigation.
Group A – Cross sectional tooth sectioning
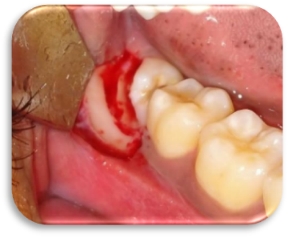
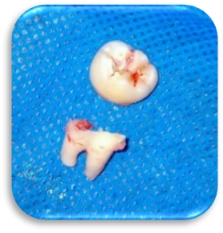
Cross-sectional method of crown cutting was used for all the patients in Group A. The crown was sectioned at the cementoenamel junction all the way from the distal aspect to mesial aspect of the crown. The crown portion was then taken out of the socket by elevating at the mesial aspect of the crown. The roots were then loosened by engaging the bifurcation and were taken out after elevating it towards the crown space. (Figure 2, Figure 3)
Group B – Longitudinal tooth sectioning
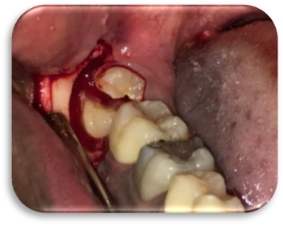
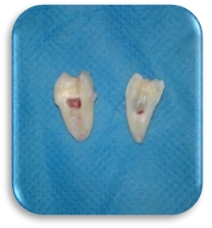
Longitudinal method of crown cutting was used for all the patients in Group B. Crown was split along the long axis from the occlusal aspect down to the furcation. Straight elevator was then used to split the tooth in to mesial and distal halves. Distal half was taken out first followed by the mesial half. (Figure 4, Figure 5)
Once the whole tooth was delivered, proper debridement of the socket was done. Wound closure was done with 3-0 resorbable sutures and post-operative instructions and medications were given.
Outcome assessment
Total operating time was recorded from the beginning of incision to the end of wound closure. Pain was assessed at the end of procedure using a visual analogue scale (VAS). Patients were recalled after 7th post-operative day and the following postoperative complications such as trismus, edema, lingual and inferior alveolar nerve paraesthesia were assessed. Trismus was evaluated by comparing the pre-operative and post-operative mouth opening. Edema was assessed by comparing pre-operative dimension A and dimension B with the post-operative measurements of the same. Lingual and inferior nerve paraesthesia was evaluated by asking the patient for subjective signs in the respective sites.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS software. The significance of difference between qualitative variables were assessed using chi square test and between quantitative variables by unpaired t test. Parametric data were expressed as mean and standard deviation (M [SD]). Statistical significance level was defined at P = 0.05.
Results
A total of 50 patients were included in this study and divided into group A (n= 25) and group B (n= 25). Group A patients underwent cross-sectional odontectomy while group B patients underwent longitudinal odontectomy. Mean age of the patients is shown in Table 1.
All the patients in the study showed uneventful healing in the postoperative visit. The results are summarized in Table 2 and comparison of postoperative pain is illustrated in Figure 1.
Table 1
Participants in the study
|
Type of odontectomy |
Mean (SD)* Age (years) |
Sex |
|
Group A- Cross sectional |
28.17(4.3) |
11 Males, 14 Females |
|
Group B- Longitudinal |
26.66(5.1) |
12 Males, 13 Females |
Table 2
Comparison of outcomes - Data in mean (SD)*
Discussion
Postoperative complications of surgical removal of impacted third molar arise from inappropriate technique and increased duration of the procedure. A thorough clinical assessment, evaluation of pre-operative radiographs and implementation of proper surgical technique are necessary to reduce the surgical morbidity. Various authors have proposed tooth sectioning techniques to reduce the surgical morbidity. Tooth sectioning facilitates elimination of retention zones and preservation of sound bone as well as vital structures nearby.7 It also minimizes the possibility of exerting too much pressure when removing wisdom teeth and also decreases resistance in the arc of rotation of a tooth.8 Though mesioangular impactions are considered as less difficult to remove, the proper method to reduce the retention zones are one of the important steps in the surgical technique.9 If the tooth cannot be removed with an elevator, the operator has to decide between continuation of bone removal and sectioning of the tooth, depending on the severity of impaction.
Removing bone to the level of cemento-enamel junction of the tooth allows access thus enabling sectioning of tooth into several segments.8 Arakeri proposed a three-piece technique, for mesioangularly impacted third molar where he sectioned the tooth into two halves, upper half did not show any resistance to elevation but the lower half which was locked under the maximum convexity of distal surface of second molar strongly resisted elevation.10 Elevation of lower segment may result in hinging of root over the neurovascular canal. Study by Cherian et al. in their “Modified Furcation to Crown tooth sectioning technique” for removing mesioangularly impacted mandibular third molars reported that duration of the procedure as well as neurosensory deficits are relatively less with modified furcation to crown tooth sectioning. They found the mean time for odontectomy in the conventional group to be 3.208 minutes while that of furcation to crown group was 2.942 minutes.11
In clinical practice, the choice of tooth sectioning would primarily be the quickest and easiest method. The primary aim of our study was to compare these two tooth sectioning techniques based on their influence on the postoperative outcomes. Only very few studies have been found in literature which clarify the relationship of tooth sectioning technique and postoperative outcomes.
Surgical edema is an expected sequela of removal of impacted teeth. Usually the 2nd or 3rd postoperative day swelling reaches a maximum level subsequently subsiding by 4th day and completely resolved by 7th day.12 The post-operative swelling as measured according to the dimensions previously stated, was found to be less in the longitudinal tooth sectioning group (Group B). All the patients were kept under the same post-operative medications suggesting that the difference in post-operative facial swelling may be determined by the following factors;
All these factors are influenced by the technique of tooth sectioning.
Longitudinal tooth sectioning facilitates removal of distal half of the tooth successfully with the guttering of buccal bone alone and thereby reduces total duration of procedure. Guttering of distal bone is additionally required to facilitate cross-sectional tooth sectioning in group A where the crown is sectioned at or just above the cemento-enamel-junction cross-sectionally and the whole crown is taken out followed by the root. If the root is bulky, the root needs to be divided again and taken out separately which may increase the duration of surgery. In group B, the tooth had to be sectioned till the furcation or just above the furcation longitudinally, split into mesial and distal halves and taken out as the same separately. Hence the additional retraction of soft tissues during distal bone guttering and more amount of bone removed in group A may contribute to post-operative edema.
In surgical removal of lower third molars, the surgeon has to work in a limited area of access contributed by the cheek, tongue, adjacent tooth and retro molar area. Because of all these inconveniences, placement of the straight micromotor handpiece in a proper direction while performing the odontectomy is always a problem. In cross-sectional method, the operator needs to place the handpiece almost perpendicular to the tooth whereas during longitudinal tooth sectioning, the handpiece is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth, which is an easier and reproducible method.
Conclusion
Even inexperienced practitioners can easily adapt the technique of longitudinal tooth sectioning, as the centre of mesio-distal width of the crown helps in orientation of odentectomy. As the crown is not removed completely, there is enough anatomical guide for the operator to proceed even after removing the distal half of the tooth. Minimizing post-operative complications always matters when surgery is in concern. Longitudinal tooth sectioning technique is a better method as it is relatively quick and reduces post-operative edema. Future studies need to be formatted to evaluate its possibility in deeper levels of impaction and other modifications that can effectively reduce the neurosensory disturbances.